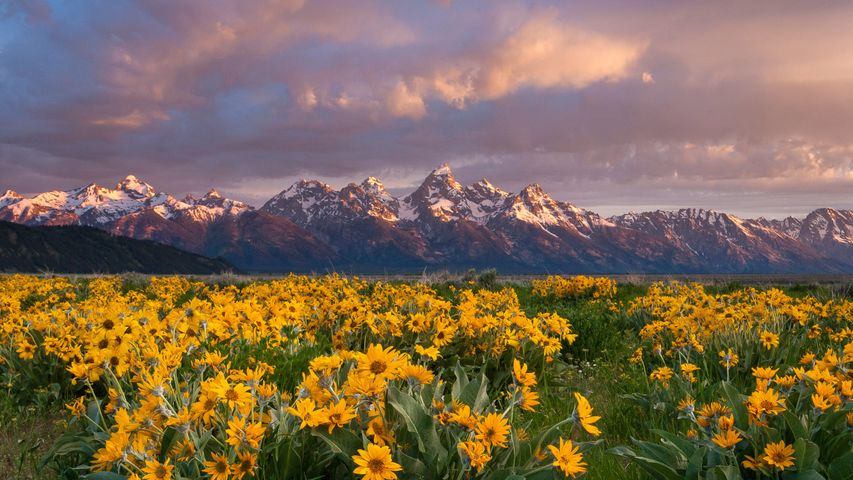
Balsamroot wildflowers bloom below the Teton Mountains in Grand Teton National Park, Wyoming
© Mike Cavaroc/Tandem Stills + Motio
A grand view. Grand Teton National Park
These arrowleaf balsamroot wildflowers, commonly known as Oregon sunflowers, have a grand view of the Grand Tetons from the valley below the towering range. The region’s harsh weather means that only the hardiest of wildflowers can survive, and the bright yellow arrowheads fit the bill. The plants are drought-tolerant, winter hardy, tenacious against trampling, and even fire-resistant, with a taproot that regenerates leaves and flowers after the top has burned.
Located just 10 miles from Yellowstone National Park, Grand Teton National Park and the surrounding national forests constitute the almost 18-million-acre (28,000-square-mile) Greater Yellowstone Ecosystem, one of the world's largest intact mid-latitude temperate ecosystems. There’s something for every lover of the outdoors here, and the park is a popular destination for mountaineering, hiking, fishing, and other forms of recreation, with more than 1,000 drive-in campsites and over 200 miles of hiking trails that provide access to backcountry camping areas. Grand Teton National Park is one of the 10 most popular parks in the United States.
Related Images
Bing Today Images
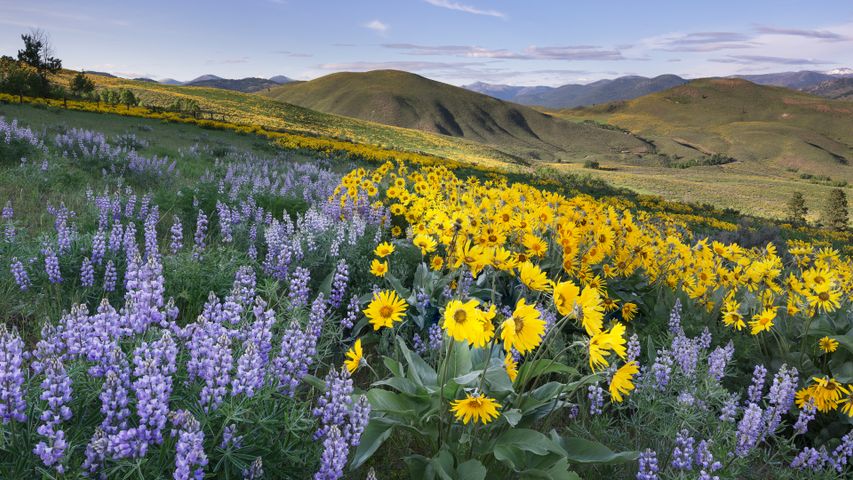


 Balsamroot and lupines, Methow Valley, North Cascades, Washington
Balsamroot and lupines, Methow Valley, North Cascades, Washington
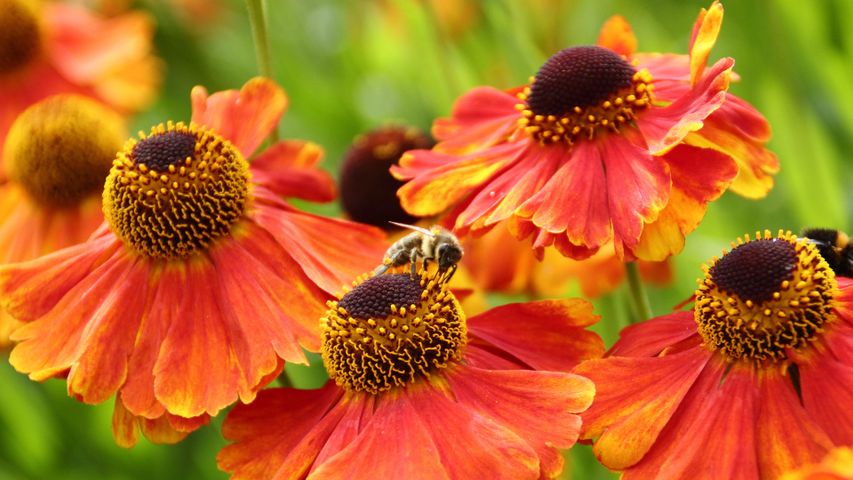 European honeybees in Sheffield, England
European honeybees in Sheffield, England
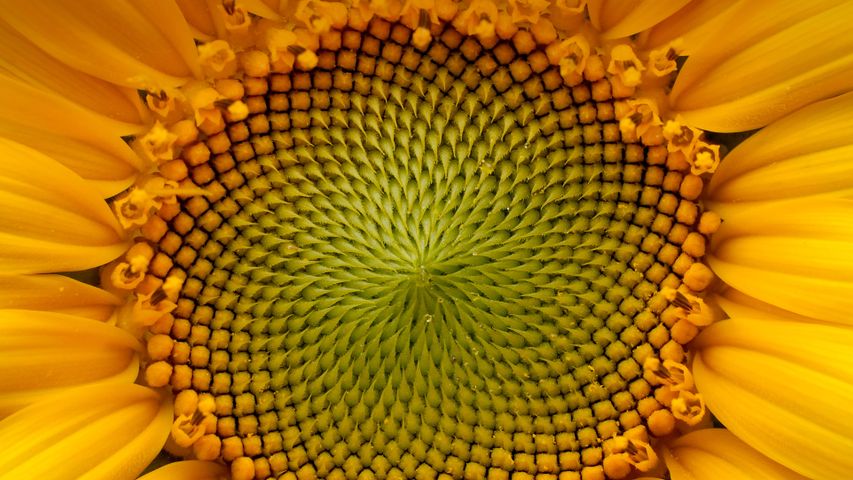 Sunflower
Sunflower
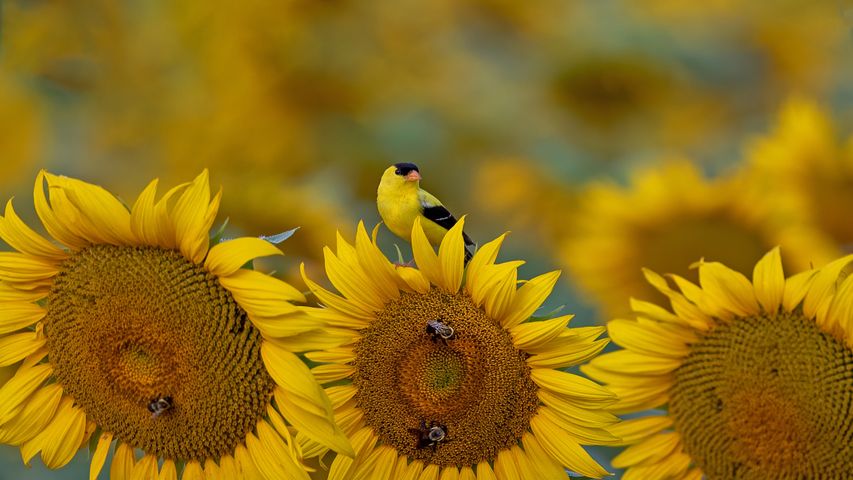 Goldfinch on a sunflower in McConnells, South Carolina
Goldfinch on a sunflower in McConnells, South Carolina
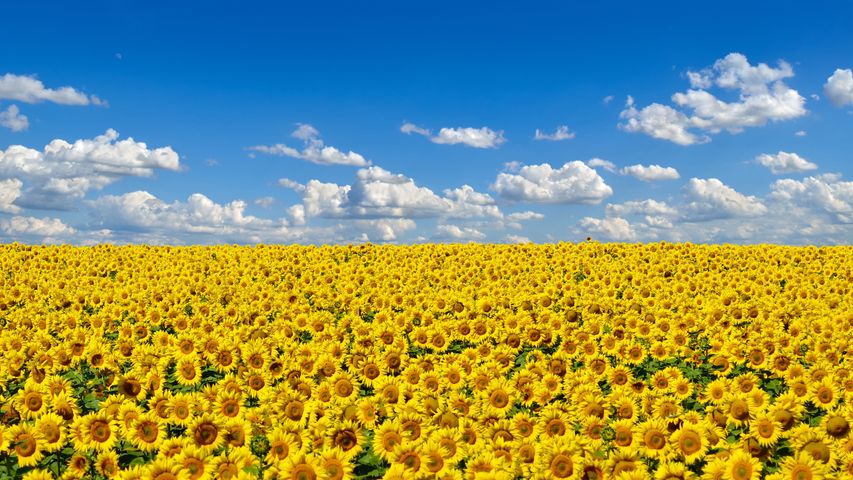 Field of sunflowers, Ukraine's national flower
Field of sunflowers, Ukraine's national flower
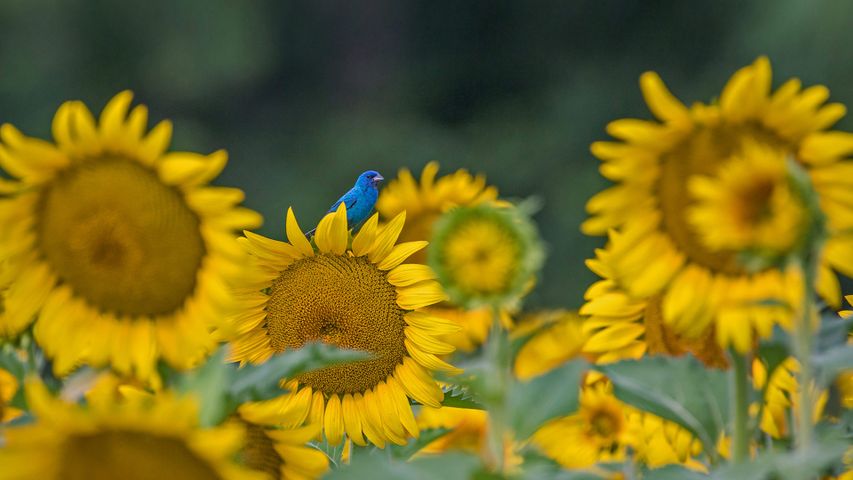 An indigo bunting on a sunflower
An indigo bunting on a sunflower
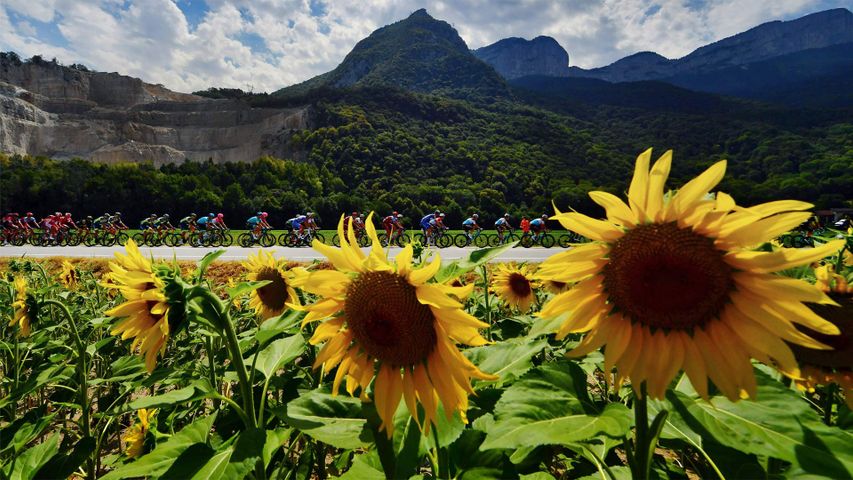 Peloton during the 2018 Tour de France in Valence, France
Peloton during the 2018 Tour de France in Valence, France
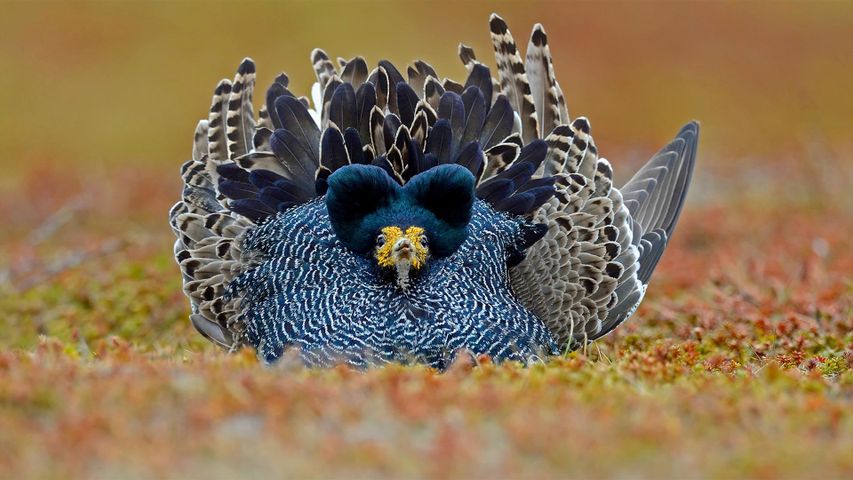 Ruff male displaying on Varanger Peninsula in Norway
Ruff male displaying on Varanger Peninsula in Norway